Here we will show you how to count by 76, discuss counting by 76 patterns, and tell you why knowing how to count by 76 matters. To start off, note that Count by 76 means counting in 76s, or count by seventy-sixes, and it is also called skip counting by 76.
How to count by 76
Normally, we would count by 1 like this: 1, 2, 3, 4, etc., but when we count by 76, we count 76, 152, 228, 304, and so on.
In other words, to count in intervals of 76 or skip counting by 76, we start with 76 and then add 76 to get the next number, and then continue adding 76 to the previous number to keep counting by 76, like this:
76
76 + 76 = 152
152 + 76 = 228
228 + 76 = 304
304 + 76 = 380
...
You can of course skip count by 76 forever, so it is impossible to make a list of all numbers, but below is a Count by 76 Chart of the first 100 numbers to get you started.
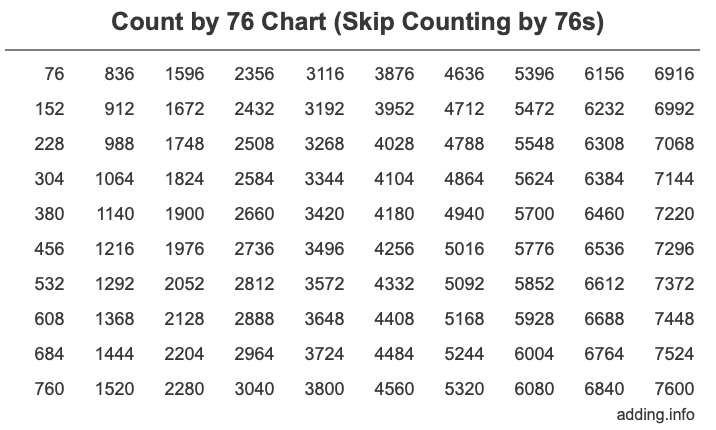
Looking at the chart above, you will see that the first column has the first ten numbers you get when you skip count by 76, the second column has the next ten numbers you get when you skip count by 76, and so forth.
Count by 76 Patterns
We organized the Skip Counting by 76s Chart above in 10 rows and 10 columns so you can easily identify patterns.
Skip counting always creates patterns. Figuring out these patterns may help you if want to count by 76, but don't have the Counting by 76s Chart above. Obviously, one pattern with counting by 76s is that the number increases by 76.
Furthermore, if you look at each row above, each number in the row has the same last digit (ones place). That means that every tenth number has the same last digit.
If you look down the columns, you will see that the last digit (ones place) repeats itself in blocks of 5 over and over. The pattern of the last digit when you count by 76 goes 6, 2, 8, 4, 0 and 6, 2, 8, 4, 0 and so on for as long as you count by 76.
Why Count by 76?
We think that understanding and learning about skip counting by 76 is important, because it teaches you how the arithmetic operations fit together. Below are some examples of what we mean.
When you count by seventy-six, you are also creating a list of multiples of 76 that you can use in math when you need the least common multiple. 76 times n equals the nth multiple or skip count of 76.
When you skip count by 76, you are also creating a list of numbers that 76 is divisible by. On top of that, skip counting by 76 is the same as making the 76 times table.
Skip Counting
Need to skip count by another number? Enter another number for us to skip count for you.
Count by 77
Here is the next number on our list that we used to skip count.
Copyright | Privacy Policy | Disclaimer | Contact